You are given an integer n. There is a complete binary tree with 2n - 1 nodes. The root of that tree is the node with the value 1, and every node with a value val in the range [1, 2n - 1 - 1] has two children where:
- The left node has the value
2 * val, and - The right node has the value
2 * val + 1.
You are also given a 2D integer array queries of length m, where queries[i] = [ai, bi]. For each query, solve the following problem:
- Add an edge between the nodes with values
aiandbi. - Find the length of the cycle in the graph.
- Remove the added edge between nodes with values
aiandbi.
Note that:
- A cycle is a path that starts and ends at the same node, and each edge in the path is visited only once.
- The length of a cycle is the number of edges visited in the cycle.
- There could be multiple edges between two nodes in the tree after adding the edge of the query.
Return an array answer of length m where answer[i] is the answer to the ith query.
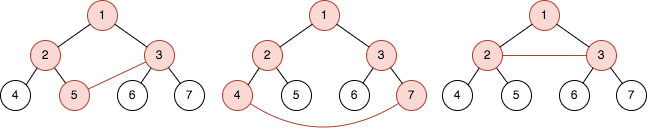
Input: n = 3, queries = [[5,3],[4,7],[2,3]] Output: [4,5,3] Explanation: The diagrams above show the tree of 23 - 1 nodes. Nodes colored in red describe the nodes in the cycle after adding the edge. - After adding the edge between nodes 3 and 5, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [5,2,1,3]. Thus answer to the first query is 4. We delete the added edge and process the next query. - After adding the edge between nodes 4 and 7, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [4,2,1,3,7]. Thus answer to the second query is 5. We delete the added edge and process the next query. - After adding the edge between nodes 2 and 3, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [2,1,3]. Thus answer to the third query is 3. We delete the added edge.
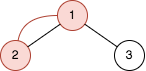
Input: n = 2, queries = [[1,2]] Output: [2] Explanation: The diagram above shows the tree of 22 - 1 nodes. Nodes colored in red describe the nodes in the cycle after adding the edge. - After adding the edge between nodes 1 and 2, the graph contains a cycle of nodes [2,1]. Thus answer for the first query is 2. We delete the added edge.
2 <= n <= 30m == queries.length1 <= m <= 105queries[i].length == 21 <= ai, bi <= 2n - 1ai != bi
impl Solution {
pub fn cycle_length_queries(n: i32, queries: Vec<Vec<i32>>) -> Vec<i32> {
let mut answer = vec![1; queries.len()];
for i in 0..queries.len() {
let mut a = queries[i][0];
let mut b = queries[i][1];
if a > b {
std::mem::swap(&mut a, &mut b);
}
answer[i] += (a.leading_zeros() - b.leading_zeros()) as i32;
b >>= a.leading_zeros() - b.leading_zeros();
answer[i] += 2 * (32 - a.leading_zeros() as i32);
for j in (0..(32 - a.leading_zeros())).rev() {
if a & (1 << j) == b & (1 << j) {
answer[i] -= 2;
} else {
break;
}
}
}
answer
}
}