- Create a root level directory called
buildSrc - Inside
buildSrccreate a file calledbuild.gradle.ktsand enable the kotlin-dsl plugin with the snippet below. Don’t forget to do a gradle sync to activate this plugin.
import org.gradle.kotlin.dsl.`kotlin-dsl`
plugins {
`kotlin-dsl`
}- Create directories
src > main > javainsidebuildSrc. - Inside java, create a Kotlin file and give it any name you want (
Dependencies.ktfor example). - Create as many object declarations as you want (ideally at least 1 for
Versionsand another forDependencies).
object Versions {
val kotlin = "1.2.21"
val support_lib = "27.0.2"
val retrofit = "2.3.0"
val rxjava = "2.1.9"
}
object Dependencies {
val kotlin_stdlib = "org.jetbrains.kotlin:kotlin-stdlib:${Versions.kotlin}"
val support_annotations = "com.android.support:support-annotations:${Versions.support_lib}"
val support_appcompat_v7 = "com.android.support:appcompat-v7:${Versions.support_lib}"
val retrofit = "com.squareup.retrofit2:retrofit:${Versions.retrofit}"
val retrofit_rxjava_adapter = "com.squareup.retrofit2:adapter-rxjava2:${Versions.retrofit}"
val rxjava = "io.reactivex.rxjava2:rxjava:${Versions.rxjava}"
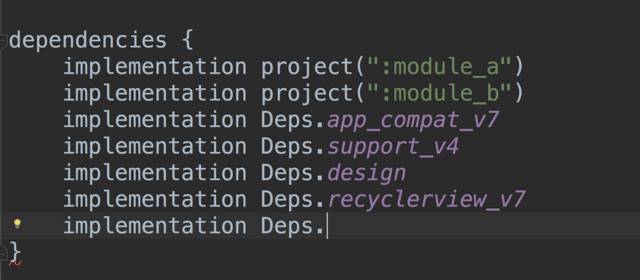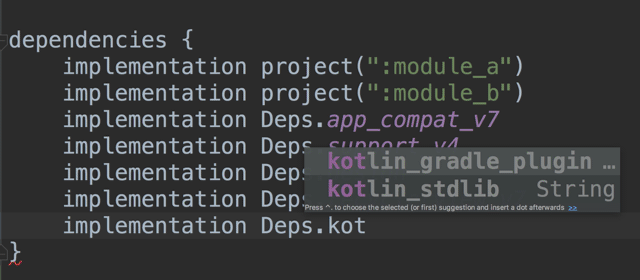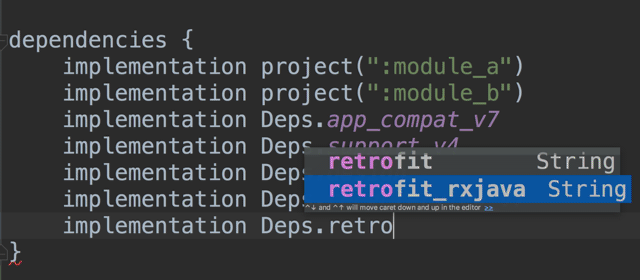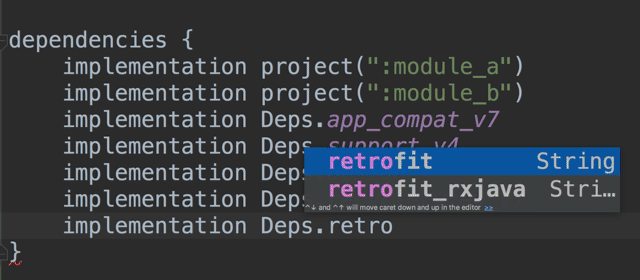
}You will be able to add this dependency straight away (with the help of autocomplete & navigation) across all of your modules with:
implementation Dependencies.kotlin_stdlib
implementation Dependencies.support_annotations
implementation Dependencies.support_appcompat_v7
implementation Dependencies.retrofit
implementation Dependencies.retrofit_rxjava_adapter
implementation Dependencies.rxjava