R scripts for Kleborate and Kaptive analysis
Here is a quick tutorial to calculate rapid raw and outbreak-adjusted proportions in your Kleborate data! This can even be performed in your terminal of choice if you want to quickly eyeball your data after a Kleborate run or PathogenWatch collection creation.
For a tutorial on how to create a PathogenWatch collection, please see the klebgenomics readme, the Klebsiella Sero-epi Shiny App or the PathogenWatch website.
In this example, I have downloaded both the Kleborate output and distance matrix from my PathogenWatch collection.
We will first load Kleborate functions for loading a single or multiple Kleborate files generated from either the the command-line version of Kleborate or Pathogenwatch.
source("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/klebgenomics/KleborateR/main/kleborate_functions.R")kleborate <- read_kleborate_file("pathogenwatch_kleborate.csv")Or if the data is from a URL...
kleborate <- read_kleborate_file("kleborate_data_maybe_from_figshare_or_github_raw_url.csv")Or if you have multiple CSVs from different runs...
kleborate <- read_kleborate_files(fs::dir_ls(glob="kleborate_*.csv"))Let's load in the cluster functions from this repo.
source("https://raw.githubusercontent.com/klebgenomics/KleborateR/main/cluster_functions.R")Now I'll read in my SNP distance matrix and calculate clusters using the default SNP distance threshold of 10. This will add a 'Cluster' column to the Kleborate data to indicate which genomes belong to the same cluster.
snps <- read_snp_diff("pathogenwatch_snp_dist.csv")
data <- get_cluster_membership_from_distmat(kleborate, snps) I can optionally change the SNP distance threshold to 20 like so:
snps <- read_snp_diff("pathogenwatch_snp_dist.csv")
data <- get_cluster_membership_from_distmat(kleborate, snps, snp_dist=20) Or just do in a one-liner:
data <- get_cluster_membership_from_distmat(readr::read_csv("pathogenwatch_kleborate.csv"), read_snp_diff("pathogenwatch_snp_dist.csv")) The data can have additional columns of metadata for performing adjusted counts such as "Country", "Site" and "Year". You can name them however you wish, but you MUST declare your cluster adjustment and epidemiological columns in the downstream functions.
Let's add a bit more metadata for cluster adjustment.
isolates_from_site1 <- c("a", "b", "c")
isolates_from_site2 <- c("x", "y", "z")
isolates_from_2009 <- c("a", "b", "c")
isolates_from_2010 <- c("x", "y", "z")
data <- data |>
dplyr::mutate(
Country = "United Kingdom",
Site = dplyr::case_when(
`Genome Name` %in% isolates_from_site1 ~ "Site1",
`Genome Name` %in% isolates_from_site2 ~ "Site2",
TRUE ~ "Site3"
),
Year = dplyr::case_when(
`Genome Name` %in% isolates_from_2009 ~ 2009,
`Genome Name` %in% isolates_from_2010 ~ 2010,
TRUE ~ 2011
),
)Now we have a bit more epidemiological information to adjust our proportions.
Let's load in the Kleborate functions from this repo.
source('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/klebgenomics/KleborateR/main/kleborate_functions.R')Let's look at the raw and outbreak-adjusted proportions of the K-locus.
get_counts(data, "K_locus")Which displays the following:
Removing K_locus from epi_vars
Grouping var: K_locus
Epi vars: ST, K_type, O_locus, O_type, Country, Study, Site, Cluster, Large_cluster
Adj vars: Cluster, Site, Study, ST
# A tibble: 140 × 14
K_locus raw_count adj_count raw_prop adj_prop n_ST n_K_type n_O_locus
<chr> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl> <int> <int> <int>
1 KL107 731 448 0.0771 0.0710 197 1 12
2 KL2 575 347 0.0606 0.0550 42 1 3
3 KL102 721 309 0.0760 0.0490 38 1 4
4 KL24 391 288 0.0412 0.0456 35 1 3
5 KL15 368 189 0.0388 0.0300 31 1 2
6 KL62 280 185 0.0295 0.0293 41 1 2
7 KL25 248 182 0.0261 0.0288 36 1 5
8 KL30 227 153 0.0239 0.0242 51 1 3
9 KL28 175 148 0.0185 0.0235 31 1 5
10 KL17 232 148 0.0245 0.0235 15 1 4
# ℹ 130 more rows
# ℹ 6 more variables: n_O_type <int>, n_Country <int>, n_Study <int>,
# n_Site <int>, n_Cluster <int>, n_Large_cluster <int>
# ℹ Use `print(n = ...)` to see more rowsNow, let's look at the raw and outbreak-adjusted proportions of each K-locus withn each ST.
raw_adj_prop(data, c("ST", "K_locus"))Which displays the following:
grouping_var: ST in adj_vars, removing from adj_vars
Grouping vars: ST, K_locus
Denominator: ST
Adj vars: Cluster, Site, Study
# A tibble: 1,973 × 6
ST K_locus raw_count adj_count raw_prop adj_prop
<chr> <chr> <int> <int> <dbl> <dbl>
1 ST307 KL102 562 189 0.988 0.964
2 ST23 KL1 126 114 1 1
3 ST101 KL17 193 113 0.877 0.856
4 ST15 KL24 147 111 0.298 0.365
5 ST15 KL112 222 111 0.449 0.365
6 ST45 KL24 142 100 0.587 0.571
7 ST14 KL2 157 96 0.720 0.686
8 ST512 KL107 252 83 1 1
9 ST20 KL28 79 76 0.669 0.667
10 ST17 KL25 97 71 0.439 0.452The output is arranged by adj_count in descending order and the default denominator is the first
variable in the vector (in this case, ST). We can make the denominator "ST" by changing the
order of the vector to c("K_locus", "ST") OR by using the denominator argument:
raw_adj_prop(data, c("ST", "K_locus"), denominator="K_locus").
From this output preview, we can see that 100% of ST23 isolates have a KL1 capsule (K) locus, consistent with published data.
Now, let's plot this data!
Let's load in the plotting functions from this repo.
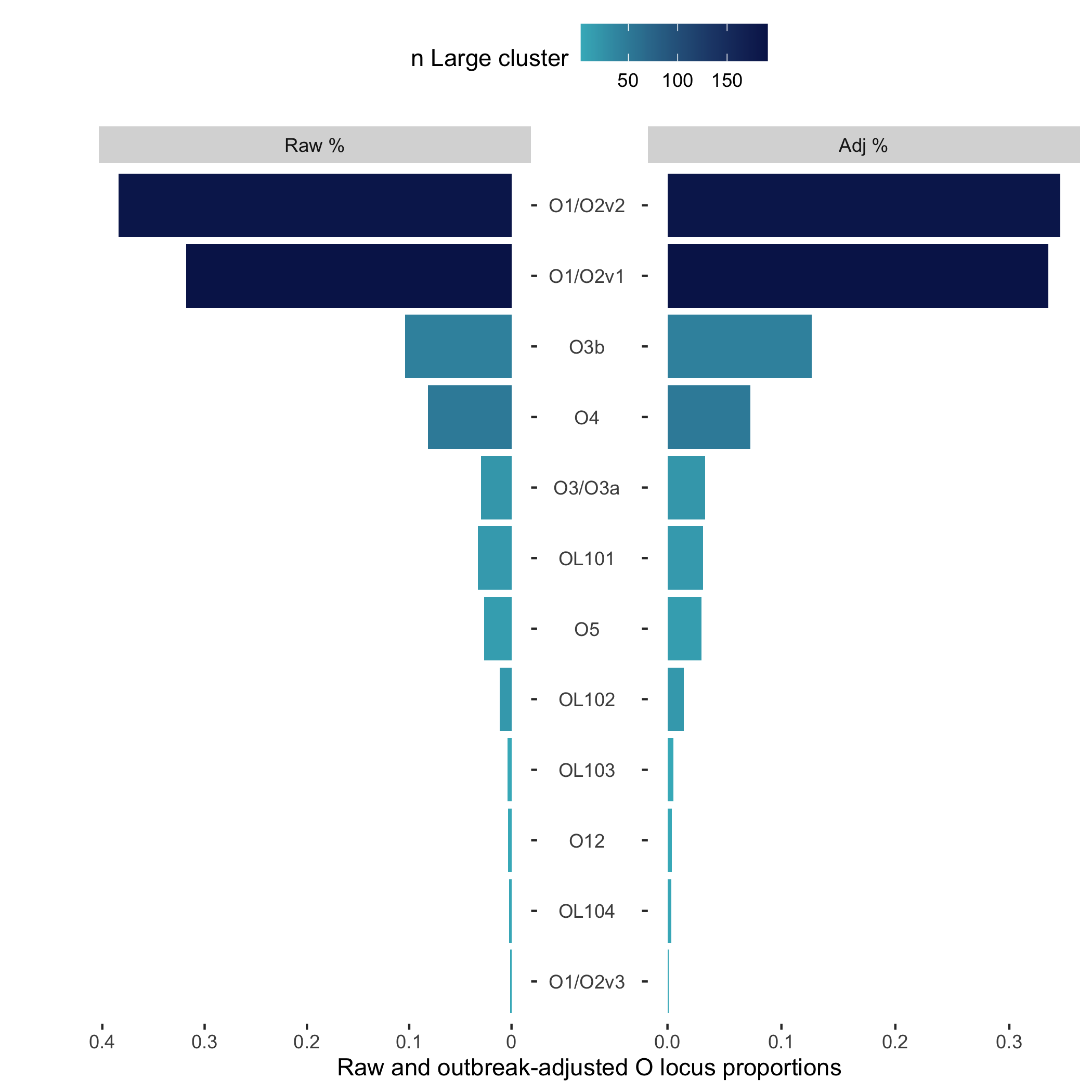
source('https://raw.githubusercontent.com/klebgenomics/KleborateR/main/plotting_functions.R')Let's plot the raw and outbreak-adjusted proportions of the O-loci in this data.
We can provide the get_counts output as an argument, or use a pipe like so!
get_counts(data, "O_locus") |> plot_raw_adj_pyramid()Which outputs the following plot: